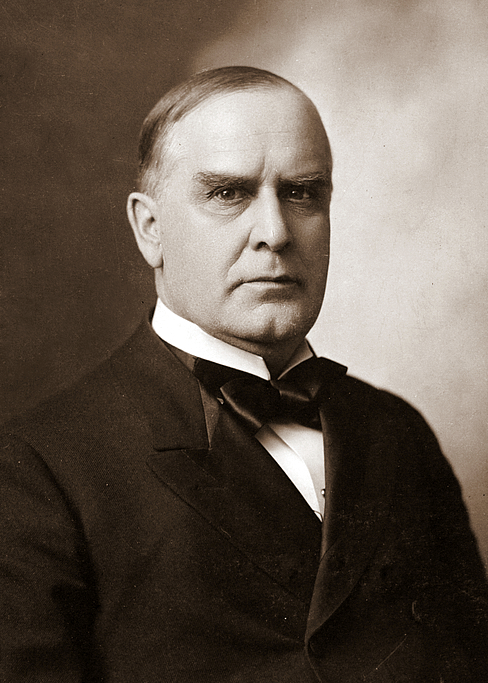University of Hawai‘i Libraries Special Collection – The 1897 Petitions Protesting Annexation by Professor Noenoe K. Silva
When William McKinley won the presidential election in November of 1896, the question of Hawaii’s annexation to the U.S. was again opened. The previous president, Grover Cleveland, was a friend of Queen Liliuokalani. He had remained opposed to annexation until the end of his term, but McKinley was open to persuasion by U. S. expansionists and by annexationists from Hawaii. He agreed to meet with a committee of annexationists from Hawaii, Lorrin Thurston, Francis Hatch and William Kinney. After negotiations, in June of 1897, McKinley signed a treaty of annexation with these representatives of the Republic of Hawaii. The President then submitted the treaty to the U. S. Senate for approval.
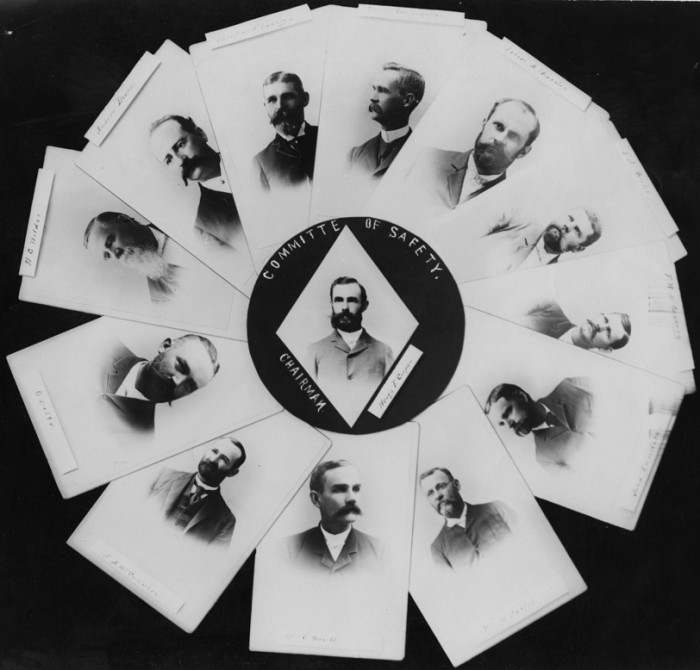
The Hui Aloha Aina for Women, the Hui Aloha Aina for Men, and the Hui Kalaiaina formed a coalition to oppose the treaty. Together, these three organizations represented a majority of the Kanaka Maoli (Native Hawaiians). Hui Kalaiaina had originally been formed after the Bayonet Constitution of 1887 as a vehicle for Kanaka Maoli political power. The two Hui Aloha Aina organizations were founded just after the overthrow of the Native government in 1893, expressly to support the Queen and to oppose U.S. annexation.
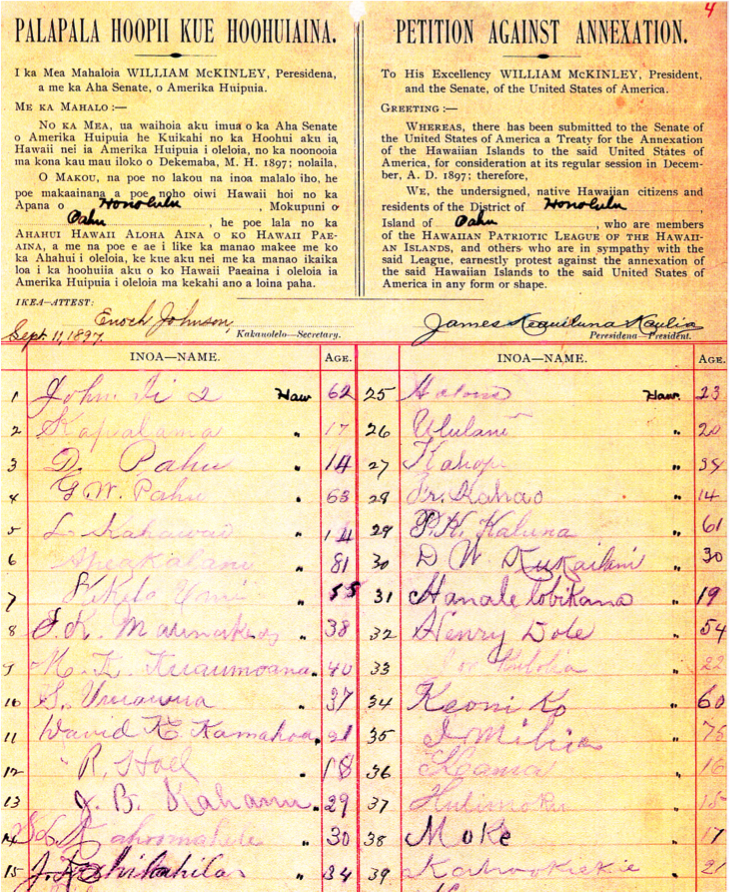
The Kanaka Maoli believed that the American government was committed to their stated principles of justice and of government of the people, by the people, and for the people. They believed that once the U.S. President and members of Congress saw that the great majority of Hawaiian citizens opposed the annexation, the principles of fairness would prevail, that is, their Native government would be restored. The three huis therefore began to organize mass petition drives The heading on Hui Aloha Aina’s petition read: PALAPALA HOOPII KUE HOOHUI AINA, Petition Protesting Annexation
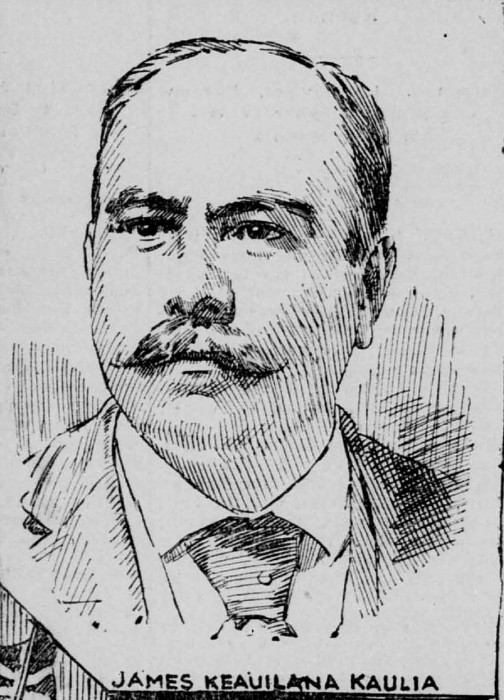 On September 6, 1897, the Hui Aloha Aina held a halawai makaainana – a mass meeting – , at Palace Square, which thousands of poe aloha aina – patriots – attended. President James Kaulia gave a rousing speech, saying “We, the nation (lahui) will never consent to the annexation of our lands, until the very last patriot lives.” He said agreeing to annexation was like agreeing to be buried alive. He predicted that annexation would open the door for many foreigners to come here, and to take jobs and resources away from the Native people. He asked, “Then where will we live?” The crowd answered, “In the mountains,” which figuratively means, “we shall be homeless.” He asserted that a mass refusal by the people could prevent the annexation: “If the nation remains steadfast in its protest of annexation, the Senate can continue to strive until the rock walls of Iolani Palace crumble, and never will Hawaii be annexed to America!” The annexationist newspapers had published threats that the leaders of the mass meeting would be arrested for treason, but Mr. Kaulia assured the people that their assembly was legal. He said that it was because the brains of the government could not push over the brains of the Kanaka Maoli that the government had to resort to weapons of war. (At this time, Hawaii was ruled by a haole – European- American – oligarchy called the Republic of Hawaii that had deprived the Native people of political participation.) He said, “Let us take up the honorable field of struggle, brain against brain.” He told the people, “Do not be afraid, be steadfast in aloha for your land and be united in thought. Protest forever the annexation of Hawaii until the very last aloha aina [lives]!” The crowd cheered.
On September 6, 1897, the Hui Aloha Aina held a halawai makaainana – a mass meeting – , at Palace Square, which thousands of poe aloha aina – patriots – attended. President James Kaulia gave a rousing speech, saying “We, the nation (lahui) will never consent to the annexation of our lands, until the very last patriot lives.” He said agreeing to annexation was like agreeing to be buried alive. He predicted that annexation would open the door for many foreigners to come here, and to take jobs and resources away from the Native people. He asked, “Then where will we live?” The crowd answered, “In the mountains,” which figuratively means, “we shall be homeless.” He asserted that a mass refusal by the people could prevent the annexation: “If the nation remains steadfast in its protest of annexation, the Senate can continue to strive until the rock walls of Iolani Palace crumble, and never will Hawaii be annexed to America!” The annexationist newspapers had published threats that the leaders of the mass meeting would be arrested for treason, but Mr. Kaulia assured the people that their assembly was legal. He said that it was because the brains of the government could not push over the brains of the Kanaka Maoli that the government had to resort to weapons of war. (At this time, Hawaii was ruled by a haole – European- American – oligarchy called the Republic of Hawaii that had deprived the Native people of political participation.) He said, “Let us take up the honorable field of struggle, brain against brain.” He told the people, “Do not be afraid, be steadfast in aloha for your land and be united in thought. Protest forever the annexation of Hawaii until the very last aloha aina [lives]!” The crowd cheered.
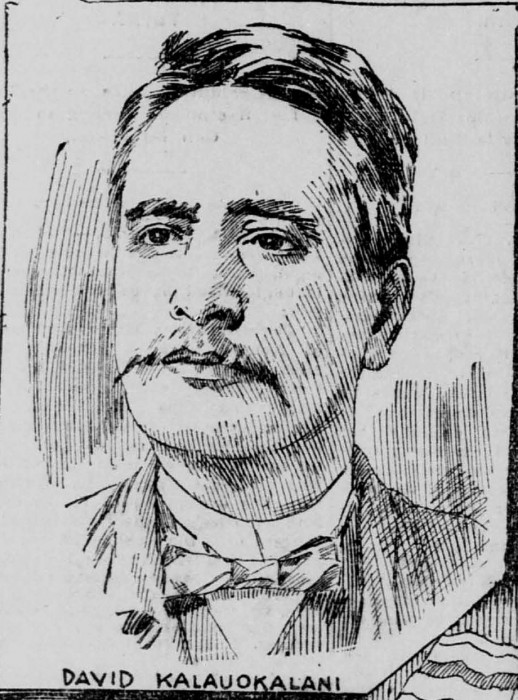 Following Kaulia, David Kalauokalani, President of the Hui Kalaiaina, explained the details of the annexation treaty to the crowd. He told them that the Republic of Hawaii had agreed to give full government authority over to the United States, reserving nothing. It would also give all the government’s money, the government and crown lands, government buildings, harbors, bays, military forts, military armaments and warships, and all resources claimed by the government of the Hawaiian Islands. Furthermore, he explained, the laws of the United States would not extend to the Hawaiian Islands, but the Congress of the U.S. would decide how Hawaii was to be governed. It was uncertain whether the Kanaka Maoli would have the right to vote. He said those who favored annexation would want to deny Kanaka Maoli voting rights because, from the very beginning, they have known that the Kanaka Maoli would overwhelmingly vote against annexation and anyone who supported it. This is the reason they were always afraid to put a vote to the people.
Following Kaulia, David Kalauokalani, President of the Hui Kalaiaina, explained the details of the annexation treaty to the crowd. He told them that the Republic of Hawaii had agreed to give full government authority over to the United States, reserving nothing. It would also give all the government’s money, the government and crown lands, government buildings, harbors, bays, military forts, military armaments and warships, and all resources claimed by the government of the Hawaiian Islands. Furthermore, he explained, the laws of the United States would not extend to the Hawaiian Islands, but the Congress of the U.S. would decide how Hawaii was to be governed. It was uncertain whether the Kanaka Maoli would have the right to vote. He said those who favored annexation would want to deny Kanaka Maoli voting rights because, from the very beginning, they have known that the Kanaka Maoli would overwhelmingly vote against annexation and anyone who supported it. This is the reason they were always afraid to put a vote to the people.
A resolution protesting the annexation was read to the crowd, who approved it. It was announced that U.S. Senator Morgan, an advocate of annexation, would be arriving soon, and that there would be another mass meeting held while he was here.

 The petition drive started at about this time. Very soon afterwards, Mrs. Abigail Kuaihelani Campbell, President of the Women’s branch of the Hui Aloha Aina, and Mrs. Emma Aima Nawahi boarded the inter-island ship the Kinau for Hilo on a signature gathering mission.
The petition drive started at about this time. Very soon afterwards, Mrs. Abigail Kuaihelani Campbell, President of the Women’s branch of the Hui Aloha Aina, and Mrs. Emma Aima Nawahi boarded the inter-island ship the Kinau for Hilo on a signature gathering mission.
On September 14, Senator Morgan and four congressmen from the U.S. indeed arrived. On the same day, Mr. Enoch Johnson and Mr. Simon Peter Kanoa boarded the Claudine for Maui, and Mrs. Kaikioewa Ulukou departed for Kauai – all bound to gather signatures on those islands. The Hui Aloha Aina paid all of their expenses.
At the same time, there was a branch of the Hui Aloha Aina active at Kalaupapa (on the island of Molokai) where people with leprosy were imprisoned. The President of the Kalaupapa branch was Mr. Robert M. Kaaoao, who not only gathered signatures on the protest petitions, but had also organized a full day’s activities to commemorate the Queen’s birthday on September 2. The activities included a prayer service; boating, swimming, running, horse, and donkey races; as well as pole climbing and apple eating contests.
When Mrs. Campbell and Mrs. Nawahi arrived in Hilo harbor, they were greeted with honors. A delegation of the Hilo chapter of the Hui, consisting of Mr. Henry West, Mrs. Hattie Nailima, Mrs. Kekona Pilipo, and Mrs. J.A. Akamu met them at the harbor. The Hilo delegation showered them with leis, and proclaimed that a Hawaiian double-hulled canoe would carry them into the harbor. They had decorated five seats on the beautiful vessel with leis of maile, lehua, and other flowers, and had a Hawaiian flag waving at the back. The people of Laupahoehoe had sent welcome gifts of opihi, limu, and fish. Mrs. Campbell and Mrs. Nawahi attended meetings of the Hui Aloha Aina all over the Hilo and Puna area, and returned with thousands of signatures.
Meanwhile Mrs. Laura Mahelona was working hard in Kona and Kau; she was the committee member delegated to gather signatures there of both men and women. She traveled from North Kona south to Kau, leaving blank petitions with instructions everywhere she went. She told the chapter presidents to get the petitions signed and return them in a few days when her ship would stop again at the same harbors. When she returned, signed petitions were ready at every harbor. When she landed at each port, she was welcomed by the women of the Hui Aloha Aina branches, carrying leis over their arms, and when she returned to the boat, her clothes couldn’t be seen because she was completely covered by leis. Mrs. Mahelona gathered 4,216 signatures.
Mrs. Kaikioewa Ulukou gathered 2,375 on the island of Kauai.
Mr. Simon P. Kanoa gathered 1,944 in the district of Hana, Maui.
When all the work was done, there were over 21,000 signatures- men’s and women’s in about equal numbers. When one considers that the population of Native Hawaiians at the time was less than 40,000, this is an impressive number.

The Hui Kalaiaina also had a substantial membership- -they conducted their own petition drive at the same time, collecting about 17,000 signatures.
The Hui Aloha Aina held another mass meeting on October 8, 1897, and at that time decided to send delegates to Washington D.C. to present the petitions to President McKinley and to the Congress.
The executive committees of the three hui met and decided to send four delegates: James Kaulia of Hui Aloha Aina, David Kalauokalani of Hui Kalaiaina, with John Richardson, and with William Auld as secretary. All four were Kanaka Maoli. This was an important sign to the nation. Some people had written in the papers that previous delegates to Washington had failed because they were not Kanaka Maoli, or because they were too wealthy to truly have the nation’s well-being in mind at all times. It is important to note that although a women’s representative did not travel to Washington, Mrs. Campbell, President of the women’s branch of Hui Aloha Aina, was part of the decision-making committee, and was viewed as a leader of the nation along with the men.
The four Elele Lahui – National Delegates – left Hawaii on November 20, 1897. In San Francisco on November 28, they commemorated La Kuokoa – Hawaiian Independence Day.
They arrived in Washington on December 6, the day that the Senate opened. They first met briefly with Queen Liliuokalani, who was staying in Washington. Then they met Senator Richard Pettigrew who took them in to the Senate’s opening ceremonies. After the ceremonies, they returned to Ebbitt House where the Queen was staying, and where they would also stay. Someone told them at that time that their trip to Washington was useless, since it was known that there 58 votes on the side of annexation, with only 2 more votes needed for the treaty to pass. They said they didn’t answer but remained as quiet as doves. They spoke amongst themselves later, however, to plan what to do.
The next day, December 7, they met again with the Queen to consider how to present the petitions. They chose the Queen as chair of their Washington committee. Together, they decided to present the petitions of Hui Aloha Aina only, because the substance of the two sets of petitions was different. Hui Aloha Aina’s was called “petition protesting annexation,” but the Hui Kalaiaina’s petitions called for the monarchy to be restored. They agreed that they did not want to appear divided, as if they had different goals.
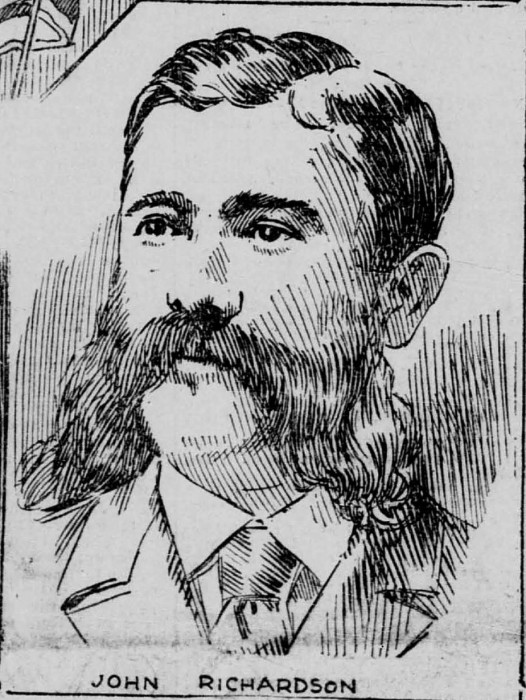 The day after that, the delegates met with Senator Hoar, who was against annexation. They braved snow, cold and slippery streets to get to the Senator’s residence. They said the “elemakule” (old man) greeted them with a handshake. He asked them what the people of Hawaii thought about annexation. John Richardson, the spokesman, explained everything. While he was explaining, they could see tears welling up in the old man’s eyes. Richardson told him that they brought petitions signed by the whole nation protesting the annexation. Senator Hoar told them to submit the petitions to him, and he would bring them before the Senate, and then to the Foreign Relations Committee. David Kalauokalani of Hui Kalaiaina also submitted his endorsement of those petitions (so that the U.S. would know both huis had the same goal). On December 9, Senator Hoar read the text of the petitions to the Senate and had them formally accepted. The delegates were present, seated in the area where people are allowed to observe the Senate proceedings.
The day after that, the delegates met with Senator Hoar, who was against annexation. They braved snow, cold and slippery streets to get to the Senator’s residence. They said the “elemakule” (old man) greeted them with a handshake. He asked them what the people of Hawaii thought about annexation. John Richardson, the spokesman, explained everything. While he was explaining, they could see tears welling up in the old man’s eyes. Richardson told him that they brought petitions signed by the whole nation protesting the annexation. Senator Hoar told them to submit the petitions to him, and he would bring them before the Senate, and then to the Foreign Relations Committee. David Kalauokalani of Hui Kalaiaina also submitted his endorsement of those petitions (so that the U.S. would know both huis had the same goal). On December 9, Senator Hoar read the text of the petitions to the Senate and had them formally accepted. The delegates were present, seated in the area where people are allowed to observe the Senate proceedings.
On December 10, the delegates met with Secretary of State John Sherman, and Kalauokalani submitted a memorial protesting annexation (Ka Memoriala a ka Lahui) to him.
In the following days, the delegates met with many different Senators and Congressmen. Senators Pettigrew and White encouraged them in the hope that the annexation treaty would be defeated. They said that they were asked a lot of questions about Japan or England trying to annex Hawaii. They answered that either of them could have taken Hawaii if they had wanted to any time in the past five years. Why would they wait for America to try before they did so? They also reminded the U.S. Congressmen that Hawaii had remained independent for fifty years, partly because of the 1843 resolution signed by Great Britain and France guaranteeing Hawaii’s independence.
By the time they left Washington on February 27, there were only 46 votes in the Senate on the pro-annexation side, down from 58 when they had arrived. Forty-six votes was far too few for the treaty to pass — sixty votes were necessary.
Senator Pettigrew and Senator Turpie insisted that the Kanaka Maoli of Hawaii be given a chance to vote on annexation. But Senator Morgan and the other pro-annexation Senators knew that if a vote were taken, it would be overwhelmingly in favor of Hawaii’s independence. In a report, these Senators wrote, “If a requirement should be made by the United States of a plebiscite [vote] to determine the question of annexation, it would work a revolution in Hawaii which would abolish its constitution.” They knew, in other words, that if the people were allowed to vote, not only would they reject annexation, they would also reject the haole Republic that had been forced upon them against their will.
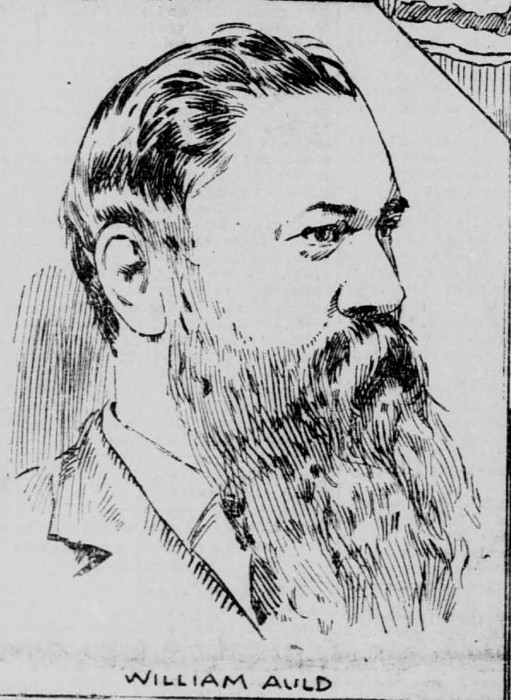 Three of the delegates, James Kaulia, David Kalauokalani, and William Auld returned to Honolulu victorious, sure that the treaty would fail, as indeed it did. They had carried the hard work and hopes of the whole nation to Washington in the form of the protest petitions. They had succeeded in persuading many senators to vote against the treaty. They left behind John Richardson to continue the work, along with Queen Liliuokalani, her secretary Joseph Heleluhe, and her devoted friend, J.O. Carter.
Three of the delegates, James Kaulia, David Kalauokalani, and William Auld returned to Honolulu victorious, sure that the treaty would fail, as indeed it did. They had carried the hard work and hopes of the whole nation to Washington in the form of the protest petitions. They had succeeded in persuading many senators to vote against the treaty. They left behind John Richardson to continue the work, along with Queen Liliuokalani, her secretary Joseph Heleluhe, and her devoted friend, J.O. Carter.
One annexation crisis was over, but another was soon to follow. This same year, the peoples of Cuba and the Philippines were fighting wars of independence against Spain. The United States also declared war on Spain after the U.S. warship, the Maine was blown up in a harbor in Cuba. The reason that the Maine was even in Cuba is questionable, since the U.S. had not been involved until it involved itself by sending the ship there. Be that as it may, the United States was at war. Suddenly, the empire- builders of the United States were saying that they needed to send military troops on ships to the Philippines to fight Spain. For this, they said they needed Hawaii. In the midst of the fever of war, a Joint Resolution of Congress called the Newlands Resolution passed by a simple majority of each house, making Hawaii a territory of the United States. That was in July of 1898; the flag of the United States was hoisted over Hawaii on August 12th.
The Kanaka Maoli continued to protest. The Hui Kalaiaina concentrated on persevering to undo the annexation, and restore the Native government. Hui Aloha Aina began to work towards securing full civil and political rights for Hawaiian citizens in the U.S. territorial system. In 1900, the two huis banded together as one political organization called the Home Rule Party. David Kalauokalani was elected President, and James Kaulia as Vice-President. This was the party that elected Robert Kalanihiapo Wilcox as (non-voting) Delegate to the U.S. Congress.
James Keauiluna Kaulia continued his work for his nation until the day of his death at age 41, in 1902. On that Sunday, he spent the morning at the jail house trying to help prisoners assert their rights. After church and lunch, he lay down for a nap from which he never woke up. He died of heart failure.
David Kalauokalani lived until 1915, also serving his people all of his life. He served as a senator in the territorial legislature, and as a member of the Board of Health. His son, also named David, became the first clerk of the City and County of Honolulu.
Mrs. Kuaihelani Campbell served as President of Hui Aloha Aina for its entire existence. She later became well-known as a benefactor for the ill and poor among her people, and for her many charitable deeds. She married Samuel Parker in 1902. Her daughter Abigail married Prince David Kawananakoa at about the same time, and Mrs. Campbell-Parker thereby became an ancestor to the royal family remaining in Hawaii today. She passed away in 1908.
Mrs. Emma Aima Nawahi kept the newspaper Ke Aloha Aina running for many years as its owner and business manager. She sold it in 1910. She also remained active in charities until her death in 1935.
The petitions protesting annexation, consisting of five hundred fifty-six pages, are now held in the National Archives in Washington D.C.
The Kanaka Maoli continue to protest today. We have never relinquished our national sovereignty. Kanaka Maoli are working on state, national, and international levels to have our existence as a nation recognized. Kanaka Maoli also continue to resist and protest every encroachment upon our inherent rights to this land, our ocean and fresh waters, and all the other natural resources of Hawaii. We are insisting as well on our rights to keep our language and cultural traditions, and the land itself, alive.
 Marama Davidson, member of Maori women’s political advocacy group Te Whare Pora Hou states, “Protectors of Mauna a Wakea have been occupying the sacred ancestral mountain on the island of Hawai‘i for over 120 days now, to prevent the construction of this telescope. We stand in solidarity with the protectors in efforts to stop this destruction. This is a direct attack on the physical, spiritual and cultural integrity of the maunga, and the wellbeing of both the environment and people.”
Marama Davidson, member of Maori women’s political advocacy group Te Whare Pora Hou states, “Protectors of Mauna a Wakea have been occupying the sacred ancestral mountain on the island of Hawai‘i for over 120 days now, to prevent the construction of this telescope. We stand in solidarity with the protectors in efforts to stop this destruction. This is a direct attack on the physical, spiritual and cultural integrity of the maunga, and the wellbeing of both the environment and people.”