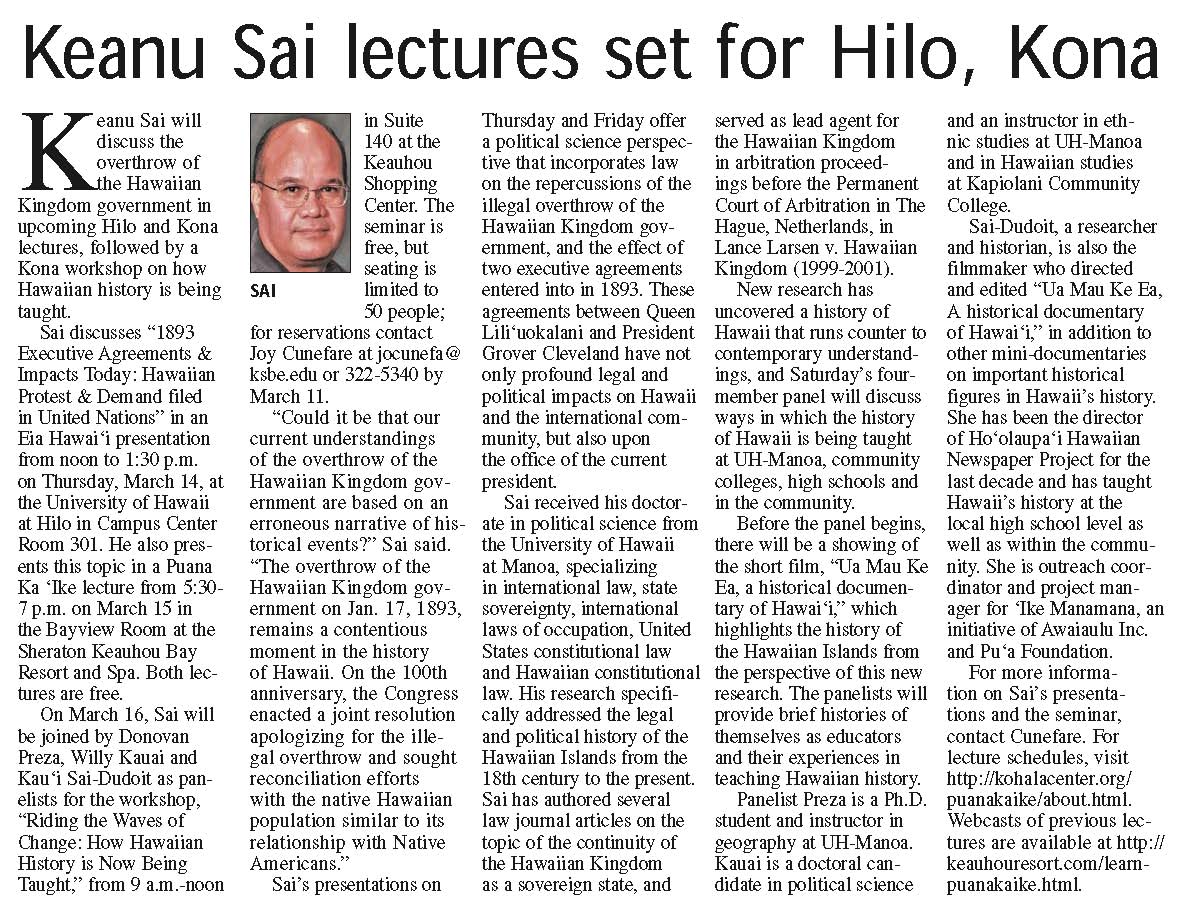
PROCLAMATION
August 21, 2013
Whereas, the Hawaiian Kingdom existed as an independent State in the nineteenth century, as acknowledged by the Permanent Court of Arbitration in 2001 by dictum in Larsen v. Hawaiian Kingdom, and that international law provides for the presumption of the Hawaiian State’s continuity, which may be refuted only by reference to a valid demonstration of legal title, or sovereignty, on the part of the United States, absent of which the presumption remains;
Whereas, because there exists no valid demonstration of legal title, or sovereignty, on the part of the United States over the Hawaiian Islands, all United States government agencies operating within the territory of the Hawaiian State that was established by the United States Congress, which includes the State of Hawai‘i and County governments, are self-declared and their authority unfounded;
Whereas, Hawaiian subjects took the necessary and extraordinary steps, by virtue of the legal doctrine of necessity and according to the laws of the country and international law, to reestablish the Hawaiian government as it stood on January 17, 1893, in an acting capacity on February 28, 1997, in order to exercise the country’s preeminent right to self-preservation during an illegal and prolonged occupation by the United States of America since August 12, 1898;
Whereas, for the past 13 years, the acting government of the Hawaiian Kingdom has been vested with a prescriptive special customary right under international law to represent the Hawaiian State during this prolonged and illegal occupation by virtue of the legal doctrine of acquiescence, as well as explicit acknowledgment by the United States of America, and other States, of the acting government’s de facto authority before the Permanent Court of Arbitration, the United Nations Security Council, and the United Nations General Assembly;
Whereas, a Brief on the Continuity of the Hawaiian State and the Legitimacy of the acting government of the Hawaiian Kingdom can be accessed online at: http://hawaiiankingdom.org/pdf/Continuity_Brief.pdf.
Now, therefore, by virtue of the authority vested in the acting government, we do hereby declare, proclaim, and make known as follows:
- The laws are obligatory upon all persons, whether subjects of this kingdom, or citizens or subjects of any foreign State, while within the limits of this kingdom, except so far as exception is made by the laws of nations in respect to Ambassadors or others. The property of all such persons, while such property is within the territorial jurisdiction of this kingdom, is also subject to the laws (§6, Civil Code). The Hawaiian Civil Code, Penal Code and the 1884 and 1886 Session Laws can be accessed online at http://hawaiiankingdom.org/constitutional-history.shtml.
- The acting government of the Hawaiian Kingdom reclaims its sovereignty over all property within the territorial jurisdiction of this kingdom by virtue of its special customary right to represent the Hawaiian State during an illegal and prolonged occupation by the United States of America.
- As a result of Hawaiian law not being complied with since January 17, 1893, all titles to real estate within the territorial jurisdiction of this kingdom are invalid and void for want of a competent notary public and registrar for the Bureau of Conveyances (§1249, §1254, §1255, §1262, §1263, §1267, Civil Code). Remedy for these defects will take place in accordance with Hawaiian Kingdom law and the international law of occupation.
Peter Umialiloa Sai, Acting Vice Chair of the Council of Regency, and Acting Minister of Foreign Affairs