Concerned She May Be Incurring Criminal Liability and Requests Corporation Counsel Opinion regarding incurring Criminal Liability
 Hilo, HI- Council member Jen Ruggles released a statement today stating she had recently come to understand that she may be in violation of her oath of office to uphold the United States constitution and may be incurring criminal liability for war crimes under both U.S. federal law and international law. She has retained Stephen Laudig as legal counsel in order to communicate with the County Corporation Counsel on this matter.
Hilo, HI- Council member Jen Ruggles released a statement today stating she had recently come to understand that she may be in violation of her oath of office to uphold the United States constitution and may be incurring criminal liability for war crimes under both U.S. federal law and international law. She has retained Stephen Laudig as legal counsel in order to communicate with the County Corporation Counsel on this matter.
Click here to download the letter to Joe Kamelamela, Hawai‘i County Corporation Counsel.
Through her attorney, Council member Ruggles has formally requested the Office of Corporation Counsel to assure her that she is not incurring criminal liability under international humanitarian law and United States Federal law as a Council member for:
- Participating in legislation of the Hawai‘i County Council that would appear to be in violation of Article 43 of the Hague Regulations and Article 64 of the Geneva Convention where the laws of the Hawaiian Kingdom must be administered and not the laws of the United States;
- Being complicit in the collection of taxes from protected persons that stem from legislation enacted by the Hawai‘i County Council, which would appear to be in violation of Article 28 and 47 of the Hague Regulations and Article 33 of the Geneva Convention where pillaging is prohibited;
- Being complicit in the foreclosures of properties of protected persons for delinquent property taxes that stem from legislation enacted by the Hawai‘i County Council, which would appear to be in violation of Article 28 and 47 of the Hague Regulations and Article 33 of the Geneva Convention where pillaging is prohibited, as well as in violation of Article 46 of the Hague Regulations and Articles 50 and 53 of the Geneva Convention where private property cannot be confiscated; and
- Being complicit in the criminal prosecution of protected persons for committing misdemeanors or felonies that stem from legislation enacted by the Hawai‘i County Council, which would appear to be in violation of 147 of the Geneva Convention where protected persons are prohibited from being unlawfully confined, and cannot be denied a fair and regular trial by a tribunal with competent jurisdiction.
Until Corporation Counsel is able to assure, under applicable laws, that Council member Ruggles is not incurring criminal liability under international humanitarian law and U.S. law, she says she will be refraining from participating in the proposing and enacting of legislation for the Hawai‘i County Council. She will continue to serve her constituents as a Council member on all other matters that do not conflict with the topics of her request to the Corporation Counsel. As soon as Corporation Counsel can assure her that no criminal liability is being incurred, she will return to legislate.
“I took an oath where I swore to support and defend the U.S. Constitution, and the constitution states that treaties are the supreme law of the land. My current understanding is that the Hague and Geneva Conventions are international treaties ratified by the United States,” Ruggles said, “and until our county attorney assures me I am not violating my oath of office, and not incurring criminal liability, I must refrain from enacting any further legislation. I am eagerly awaiting his response. In the meanwhile my constituents can be assured that I am still available to them, will continue to focus on our district and stand up for our disadvantaged populations.”
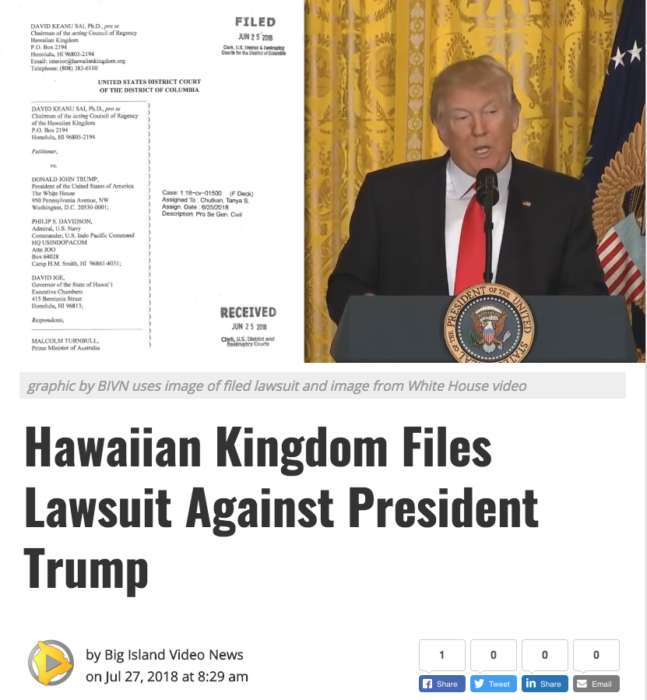
Her attorney, Stephen Laudig, states that Ruggles had been made aware of the history of the United States’ occupation of the Hawaiian Kingdom when she received an email from the Hawaiian Kingdom acting Council of Regency informing her, and all other Hawaii legislators, of several legal actions substantiating the continued existence of the Hawaiian Kingdom as a sovereign and independent State. Among the legal actions were the Larsen v. Hawaiian Kingdom proceedings held under the auspices of the Permanent Court of Arbitration, The Hague, Netherlands; the United Nations Independent Expert, Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, Dr. Alfred deZayas’ memorandum to the members of the judiciary of the State of Hawai‘i dated February 25, 2018; and the more recent lawsuit of David Keanu Sai, as Chairman of the Council of Regency v. Donald Trump, as President of the United States that was filed with United States District Court for the District of Columbia on June 15, 2018 addressing the failure of the United States to administer the laws of the Hawaiian Kingdom under Article 43 of the 1907 Hague Regulations and Article 64 of the 1949 Geneva Convention.
Ruggles says she then sought to verify the claims made by the chair of the Hawaiian Kingdom’s Acting Council of Regency, Dr. Keanu Sai, and has found his research to be thorough and comprehensive as to the explanation of legal facts describing the events leading up to and during the commencement of the illegal occupation of the Hawaiian Kingdom. She also became aware that in seven different criminal and civil cases, Dr. Sai was acknowledged and admitted as an expert witness on the subject of the continuity of the Hawaiian Kingdom as an independent State and international laws. Three of those cases were held on Hawai‘i Island in the Third Circuit.
The turning point that got Ruggles to take action was the United Nations Independent Expert’s memorandum to State of Hawai‘i officials and the lawsuit filed in Washington, D.C. In his memorandum, the Independent Expert stated, “I have come to understand that the lawful political status of the Hawaiian Islands is that of a sovereign nation-state in continuity; but a nation-state that is under a strange form of occupation by the United States resulting from an illegal military occupation and a fraudulent annexation.” He goes on to state that “As such, international laws (the Hague and Geneva Conventions) require that governance and legal matters within the occupied territory of the Hawaiian Islands must be administered by the application of the laws of the occupied state (in this case, the Hawaiian Kingdom), not the domestic laws of the occupier (the United States).”
Ruggles’ says she views the Independent Expert’s statements as authoritative under international law especially from the fact that when Dr. deZayas was elected by the United Nations Human Rights Council in 2012, the United States was a member and did not dispute his appointment.
Consequently, council member Ruggles says she began to question her own position as an elected official who swore to support and defend the constitution of the United States as to whether or not she is incurring criminal liability for enacting United States law as a legislator, which appears to be in conflict with Article 43 of the 1907 Hague Regulations and Article 64 of the 1949 Fourth Geneva Convention which mandates the occupying State (United States) to administer the laws of the occupied State (Hawaiian Kingdom).
Ruggles says, “I want it to be clear that this action, on my part should not be construed as a publicity stunt but is rather acting upon the advice of counsel given the awareness she has regarding alleged war crimes, and the awareness other State of Hawai‘i officials had and remained silent.” Ruggles says she “is a firm believer in the rule of law and not the politics of power.”






 on business, and became interested in the native people and their government. After a candid examination of the controversies existing between their own countrymen and the Hawaiian Government, they became convinced that the latter had been unjustly accused. Sir George offered to loan the government ten thousand pounds in cash, and advised the king to send commissioners to the United States and Europe with full power to negotiate new treaties, and to obtain a
on business, and became interested in the native people and their government. After a candid examination of the controversies existing between their own countrymen and the Hawaiian Government, they became convinced that the latter had been unjustly accused. Sir George offered to loan the government ten thousand pounds in cash, and advised the king to send commissioners to the United States and Europe with full power to negotiate new treaties, and to obtain a guarantee of the independence of the kingdom.
guarantee of the independence of the kingdom. Mr. Richards also received full power of attorney for the king. Sir George left for Alaska, whence he traveled through Siberia, arriving in England in November. Messrs. Richards and Haalilio sailed July 8th, 1842, in a chartered schooner for Mazatlan, on their way to the United States*
Mr. Richards also received full power of attorney for the king. Sir George left for Alaska, whence he traveled through Siberia, arriving in England in November. Messrs. Richards and Haalilio sailed July 8th, 1842, in a chartered schooner for Mazatlan, on their way to the United States* Secretary of State, from whom they received an official letter December 19th, 1842, which recognized the independence of the Hawaiian Kingdom, and declared, “as the sense of the government of the United States, that the government of the Sandwich Islands ought to be respected; that no power ought to take possession of the islands, either as a conquest or for the purpose of the colonization; and that no power ought to seek for any undue control over the existing government, or any exclusive privileges or preferences in matters of commerce.” *
Secretary of State, from whom they received an official letter December 19th, 1842, which recognized the independence of the Hawaiian Kingdom, and declared, “as the sense of the government of the United States, that the government of the Sandwich Islands ought to be respected; that no power ought to take possession of the islands, either as a conquest or for the purpose of the colonization; and that no power ought to seek for any undue control over the existing government, or any exclusive privileges or preferences in matters of commerce.” * they had been preceded by the Sir George Simpson, and had an interview with the Earl of Aberdeen, Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs, on the 22d of February, 1843.
they had been preceded by the Sir George Simpson, and had an interview with the Earl of Aberdeen, Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs, on the 22d of February, 1843.







